Manchester City
Here’s how the UEFA’s FFP rules affect Manchester United and Man City
Presently, Financial Fair Play is a subject of scrutiny, and MEN Sport has examined the impact of UEFA’s regulations on Manchester United and Manchester City.
An investigation is presently underway into allegations that Manchester City violated 115 Premier League Financial Fair Play (FFP) charges between 2009/10 and 2017/18.
Should City be convicted of the charges that have been presented against them, they could potentially face severe penalties, including relegation from the premier league. While under investigation, the Blues will exercise caution to avoid violating any additional FFP regulations to which they are obligated.
Naturally, both Manchester United and City are subject to the regulations set forth by UEFA, which function in a distinct manner from that of the Premier League FFP. This framework was revised in 2022, and MEN Sport has examined the implications of these regulations for the two Manchester clubs.
What are the prevailing regulations?
The purpose of UEFA’s announcement of these new FFP regulations a year ago was to ensure that clubs are “stable, solvent, and maintaining cost control.” The ‘three pillars’ comprised the regulations in this manner: the squad cost rule, the football revenue rule, and the no overdue payables rule.
The prohibition against past-due payables
The purpose of implementing this regulation was to prevent solvency concerns. This implies that during the licence season, any payments owed to football clubs, employees, social/tax authorities, and UEFA that are due to be settled by 30 June, 30 September, and 31 December must be settled by the club by 15 July, 15 October, and 15 January correspondingly.
If these payments are not received within a period of 90 days, UEFA is probable to initiate legal proceedings.
The rule of football revenue
A fundamental consequence of this regulation is that clubs are now obligated to finance pertinent investments, such as those in infrastructure or youth development, with pre-existing equity or contributions. This was implemented in an effort to prevent organizations from incurring debt through upgrade expenditures.
The rule of squad costs
The most significant change made by UEFA was the implementation of this rule, which limits the amount of money major clubs such as United and City can spend on teams. The governing authority aims to reduce squad expenditures to 70% of the club’s total revenue.
Nonetheless, they have chosen to adopt a methodical approach. This season, both City and United are permitted to spend 90% of their revenue. By the following season, that percentage will decline to 80%, and it will ultimately reach 70% in 2025/26.
What are the consequences of rule violations?
Each pillar is subject to a unique set of sanctions.
The no-delinquent payables prohibition
The penalties that have been imposed on these have recently been specified as having been increased by the Club Financial Control Body (CFCB).
The sanction on football profits
A club that is convicted of violating this regulation may be granted the opportunity to negotiate a settlement agreement with UEFA.
The cost of sanction for the squad
The nature of these sanctions is intentionally ambiguous; they are contingent on the frequency and gravity of violations committed over a span of four years.
-
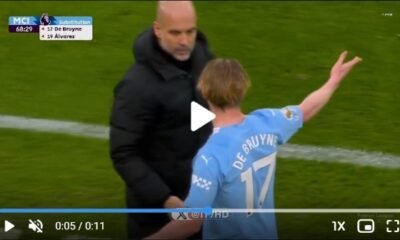
 Manchester City12 months ago
Manchester City12 months agoWatch Manchester City best Midfielder Kevin De Bruyne angry expression with Pep Guardiola substituting him in the 68th minute of the match vs Liverpool
-

 Other News1 year ago
Other News1 year agoReason why Liverpool player Darwin Nunez was held back by Jurgen Klopp from angryily attacking Pep Guardiola after the final whistle during the match
-

 Arsenal11 months ago
Arsenal11 months agoReason why Bukayo Saka might be forced to retire from football before he turned 24-year-old
-

 Manchester United11 months ago
Manchester United11 months agoMain reason Amad was sent off during Manchester United vs Liverpool FA Cup quarter-final match
-

 Arsenal1 year ago
Arsenal1 year agoI begged Him to go with Arsenal, but He went with Man United instead of us. William Saliba announced that his £45 million international teammate had chosen to join Man United over Arsenal on a personal basis.
-

 Liverpool11 months ago
Liverpool11 months agoBetween Liverpool, Manchester City and Arsenal Ian Wright reveals the club who will win the Premier League title this season
-
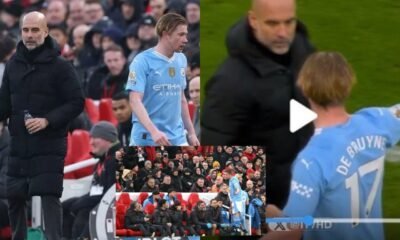
 Liverpool12 months ago
Liverpool12 months agoManchester City manager Pep Guardiola break silence and make responds to Kevin De Bruyne “not impressive angry behaviour” after Man City vs Liverpool substitution
-

 Manchester United1 year ago
Manchester United1 year agoWatch Goal Video: Manchester United vs Everton – Alejandro Garnacho scores the best goal of the year with a back flip













